Once formed these vesicles are filled with neurotransmitters and sent toward an area of the plasma membrane called the active zone. Fluid and electrolyte balance is a dynamic process that is crucial for life and homeostasis.
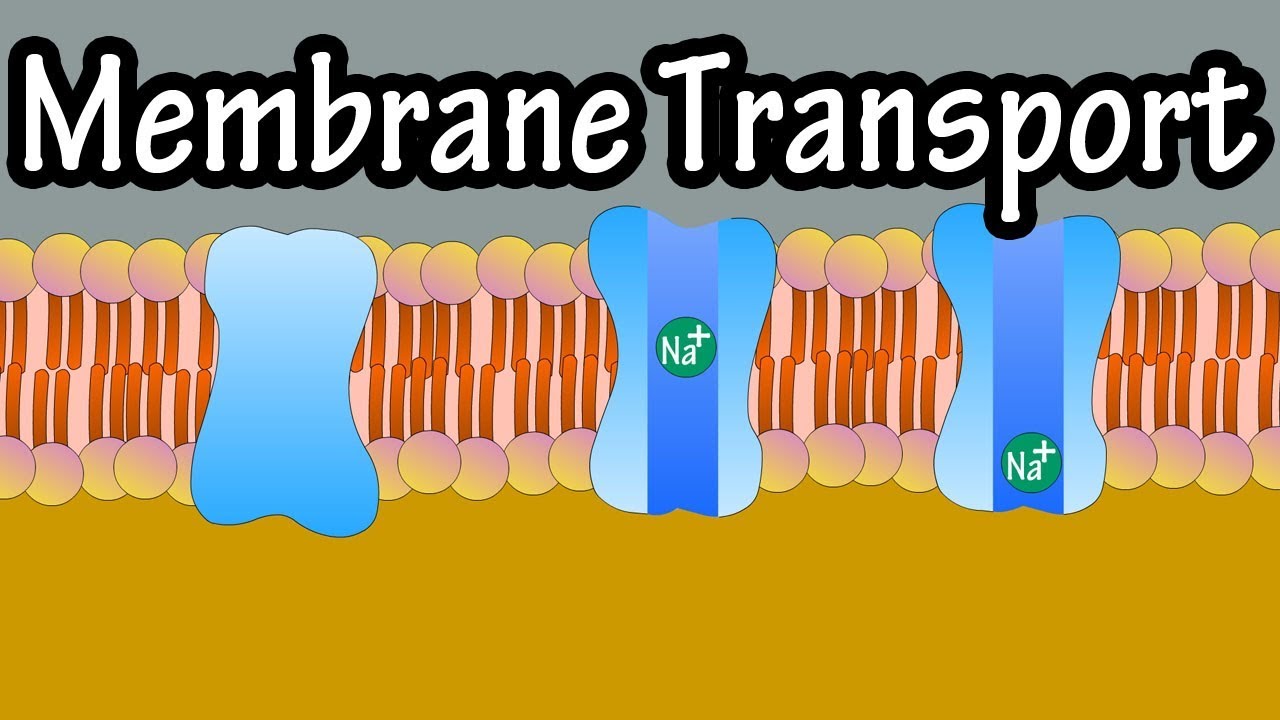
Cell Membrane Transport Transport Across A Membrane How Do Things Move Across A Cell Membrane Youtube
The cell membranes four primary functions include cell signaling selective transport excretion of wastes and structural support.

. For instance take two flasks and fill one with a mild sugar solution and the other with a. Bacterial cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan. Body fluid is located in two fluid compartments.
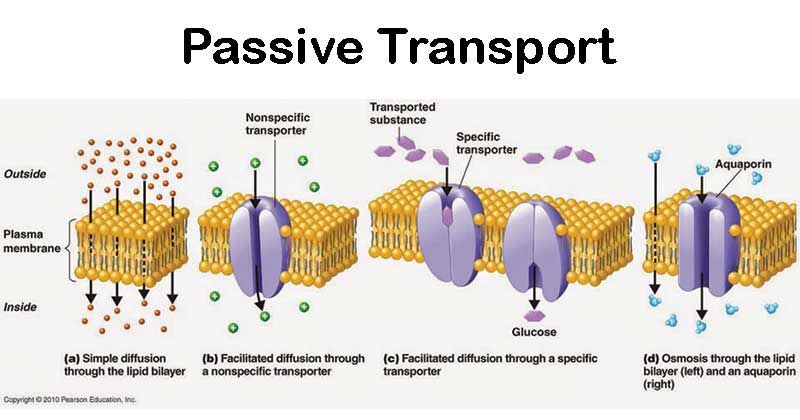
It extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is composed of similar proteins in the various organisms. Active transport is the movement of a substance across a membrane against its concentration gradient. This is usually to accumulate high concentrations of molecules that a cell needs such as glucose or amino acids.
Cell transport refers to the movement of substances across the cell membrane. People and objects move from one location to another they cross or are contained within certain boundaries and they provide a constant flow as part of larger activity. It is often described as the plasma membrane.
This quiz is all. Cell membranes are semi-permeable barrier separating the inner cellular environment from the outer cellular environment. Transport across cell membrane is classified into four ways.
The fundamental structure of the membrane is the phospholipid bilayer which forms a stable barrier between two aqueous compartments. A concentration gradient is the difference in concentration of a substance between two areas. The movement of these ions allows for changes in membrane potential or the cells charge relative to the environment.
Actual fusion of the vesicle with the pre-synaptic membrane does not. The cell membrane or plasma membrane is the structure that keeps cytoplasm from spilling out of a cell. The flow of water through a semi-permeable membrane is referred to as osmosis.
Since the cell membrane is. Cell membrane acts as a barrier to most but not all molecules. Cell Membrane.
If the cell membrane fails to function normally the cell dies. The synaptic vesicle awaits a signal an influx of calcium ions brought on by an action potential which allows the vesicle to dock at the pre-synaptic membrane. Neurons rely on depolarization.
The deformation then pinches off from the membrane on the inside of the cell creating a vesicle containing the captured substance. In eukaryotes it is composed of three main components microfilaments intermediate filaments and. Like all other cellular membranes the plasma membrane consists of both lipids and proteins.
Ion channels for example allow the passage of inorganic ions such as Na K Ca 2 and Cl-across the plasma membrane. Analogously a plasma membranes functions involve movement within the cell and across. Examples of excitable cells include.
The plasma membrane creates a small deformation inward called an invagination in which the substance to be transported is captured. The intracellular space and the extracellular space. Figure 81 Despite its seeming hustle and bustle Grand Central Station functions with a high level of organization.
Cell membrane regulates movement of substance into and out of the cell. Phagocytosis It is a process by which the. Fluid occupies almost 60 of the weight of an adult.
Endocytosis It is a process by which the large number of particles are taken with forming the vesicle into the cell It is classified into. The movement is a result of a concentration gradient that forms around the plasma membrane. Diffusion Passive Transport 2.
Rather they can be selectively opened and. The cytoskeleton is a complex dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells excluding bacteria and archaea. Cell wall In bacteria and plant cells the outermost cell cover present outside the plasma membrane is the cell wall about which we shall study now.
If the process uses chemical energy such as adenosine triphosphate ATP it is called primary active transport. The final mechanism for movement across the plasma membrane into the cell is endocytosis a process in which a small patch of plasma membrane encloses particles or tiny volumes of fluid that are at or near the cell surface. This membrane is composed of phospholipids which form a lipid bilayer that separates the contents of a cell from the extracellular fluidThe lipid bilayer is semi-permeable meaning that only certain molecules are able to diffuse across the.
VESICULAR TRANSPORT It is the transport of membrane bounded substances moving across plasma membrane It is classified into. Because the membrane does not allow all molecules to pass through it osmosis is a selective process. In the case of the plasma membrane these compartments are the inside and the outside of the cell.
Typically water is the sole free-flowing molecule across this barrier. Proteins embedded within the phospholipid bilayer. Electrolytes in body fluids are active chemicals or cations that carry positive charges and anions that carry negative.
It is a thin flexible coating around the cells of all living things. Endocytosis is a pathway for internalizing solid particles cell eating or phagocytosis small molecules and. Secondary active transport involves the use of an.
The membrane enclosure then sinks into the cytoplasm and pinches off from the membrane forming a vesicle that moves into the cytoplasm. The pores formed by these channel proteins are not permanently open. Once open channel proteins form small pores through which ions of the appropriate size and charge can cross the membrane by free diffusion.

Chapter 3 Movement Of Substances Across The Plasma Membrane By Pardip Sidhu
Chapter 7 Transport Across Cellular Membranes In Fundamentals Of Cell Biology On Openalg
Transport Of Substances Across Cell Membranes Deranged Physiology
0 Comments